CHE COSA STA CERCANDO?
CHE COSA STA CERCANDO?
I progettisti si concentrano su diversi fattori critici durante lo sviluppo cablaggio ad alta tensione per autoveicoli Sistemi per veicoli a energia rinnovabile. Risolvono problemi di connettori e terminazioni, difetti di fabbricazione e stress ambientale, che spesso causano guasti come contatti corrosi, connessioni allentate e rotture dei cavi. La selezione dei materiali gioca un ruolo fondamentale. Ad esempio:
Tipo di materiale | Proprietà chiave | Impatto su efficienza e sicurezza |
|---|---|---|
Poliolefina reticolata (XLPO) | Resistenza al calore superiore, eccellente resistenza meccanica, durata, stabilità chimica | Previene le perdite elettriche, resiste alle sollecitazioni ad alta tensione, migliora la durata e la resistenza meccanica per un funzionamento sicuro nei veicoli elettrici |
Una progettazione e una selezione adeguate aumentano la sicurezza, l'efficienza e l'affidabilità del veicolo.
I cablaggi ad alta tensione devono dare priorità alla sicurezza attraverso una progettazione e una selezione dei materiali adeguate per prevenire guasti.
L'utilizzo di un design a doppia rotaia aumenta l'affidabilità prevenendo perdite elettriche e garantendo il funzionamento continuo in caso di guasto di una rotaia.
Un isolamento e una schermatura efficaci sono essenziali per ridurre al minimo le interferenze elettromagnetiche e mantenere l'integrità del sistema.
La manutenzione regolare e le caratteristiche di accessibilità dei cablaggi semplificano le riparazioni e prolungano la durata dei connettori.
Il rispetto degli standard di settore per i connettori garantisce compatibilità, sicurezza e prestazioni affidabili nei veicoli alimentati a nuova energia.
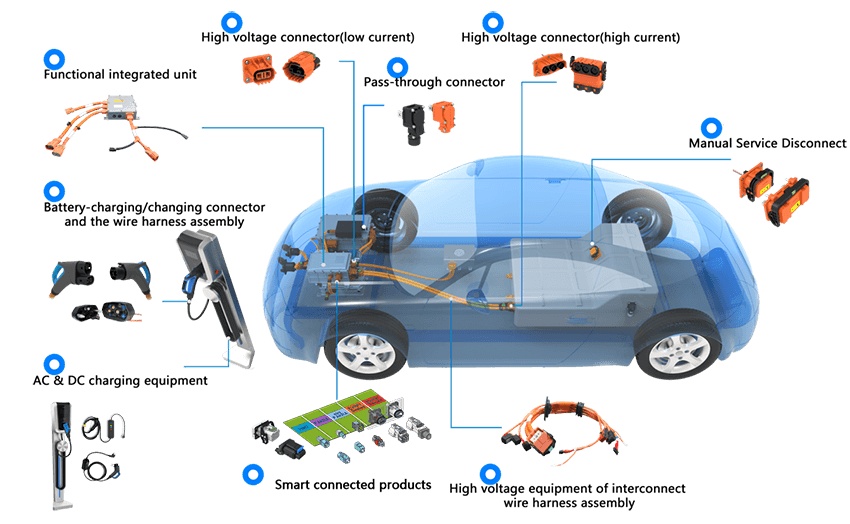
Gli ingegneri automobilistici danno priorità all'architettura di sistema quando progettano cablaggi ad alta tensione per veicoli alimentati da nuove energie. Il design a doppio binario si distingue come una caratteristica di sicurezza critica. Questa architettura impedisce ai circuiti ad alta tensione di utilizzare il telaio del veicolo come percorso di ritorno. In questo modo, elimina il rischio di perdite elettriche e potenziali pericoli. I sistemi a doppio binario introducono anche ridondanza. In caso di guasto di un binario, il sistema continua a funzionare, il che aumenta l'affidabilità e garantisce un'erogazione di energia ininterrotta.
Le pratiche di progettazione standardizzate aiutano i produttori ad abbreviare i cicli di sviluppo e a ridurre i costi. Il continuo sviluppo di materiali migliora ulteriormente l'efficienza dei costi. La precisione nella progettazione rimane fondamentale per la sicurezza, soprattutto nei sistemi ad alta tensione. Il rispetto di standard rigorosi garantisce l'affidabilità del veicolo e prestazioni ottimali. Gli ingegneri devono comprendere questi standard per garantirne la conformità durante tutto il processo di sviluppo.
L'isolamento e la schermatura costituiscono la spina dorsale della sicurezza e della compatibilità elettromagnetica (EMC) nei cablaggi ad alta tensione. Gli ingegneri selezionano materiali isolanti con proprietà elettriche superiori, come la poliolefina reticolata e i polimeri avanzati. Questi materiali resistono alle alte tensioni e prevengono le perdite elettriche.
Le tecniche di schermatura svolgono un ruolo fondamentale nel ridurre al minimo le interferenze elettromagnetiche (EMI). Le configurazioni più comuni includono strati di treccia di filo schermato, combinazioni di treccia di filo schermato e foglio di alluminio, e reti intrecciate o tubi di alluminio. Una corretta messa a terra della schermatura previene le interferenze provenienti da segnali esterni. Gli ingegneri evitano punti di messa a terra multipli per eliminare differenze di potenziale che potrebbero indurre interferenze indesiderate.
Suggerimento: la scelta di connettori con schermatura integrata garantisce una connessione continua tra il cavo e il cablaggio, creando un circuito chiuso durante la crimpatura e riducendo ulteriormente le interferenze elettromagnetiche.
I produttori implementano la schermatura intrecciata nei cablaggi per contrastare le forti interferenze elettromagnetiche (EMI). Questo approccio, abbinato ai connettori schermati, preserva l'integrità del sistema e protegge i componenti elettronici sensibili.
La sicurezza rimane la massima priorità nella progettazione dei cablaggi ad alta tensione. Gli ingegneri affrontano diversi rischi attraverso strategie di progettazione ponderate. La tabella seguente riassume i rischi per la sicurezza più comuni e le relative strategie di mitigazione:
Rischio per la sicurezza | Strategia di mitigazione del design |
|---|---|
Esposizione ad alte temperature | Evitare le zone ad alta temperatura per evitare la fusione o l'invecchiamento del filo. |
Vibrazione | Progettare la disposizione dei cablaggi in modo da evitare aree soggette a forti vibrazioni e garantire collegamenti adeguati. |
Piegatura impropria dei fili | Mantenere raggi di curvatura adeguati per evitare un aumento della resistenza e danni all'isolamento. |
Ingresso di acqua e polvere | Implementare misure di sigillatura tra i connettori per garantire prestazioni impermeabili e antipolvere. |
I produttori bilanciano il controllo dei costi con i requisiti di sicurezza riducendo al minimo la lunghezza e il peso dei cavi. Garantiscono la conformità alle normative di sicurezza e selezionano connettori di alta qualità. I cablaggi a doppio binario e l'efficace schermatura contribuiscono a mitigare le interferenze elettromagnetiche mantenendo al contempo l'efficienza dei costi.
Gli ingegneri tengono conto dell'occultamento e del rispetto delle normative anticollisione. Implementano misure di protezione per prevenire perdite elettriche e incendi. Una corretta disposizione dei componenti tiene conto dei rischi per gli occupanti e garantisce un funzionamento sicuro. Fattori chiave come la tensione di esercizio, la temperatura di esercizio, l'aumento di temperatura, il diametro dei cavi, la protezione dei cavi e la scelta dei connettori guidano il processo di progettazione.
Nota: la progettazione standardizzata e la distribuzione continua dei materiali non solo migliorano la sicurezza, ma contribuiscono anche a notevoli risparmi sui costi per i produttori.
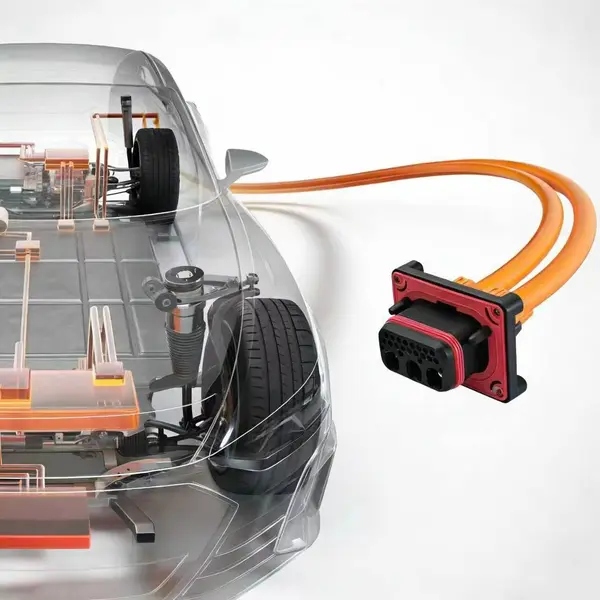

Gli ingegneri pianificano con precisione il posizionamento dei cablaggi ad alta tensione. Considerano i percorsi più brevi e sicuri tra i componenti. Questo approccio riduce le perdite di energia e migliora la gestione termica. La fluidodinamica computazionale (CFD) aiuta a identificare i punti caldi termici. Un corretto instradamento può ridurre le temperature di 8-12 gradi Celsius. I progettisti evitano il passaggio parallelo di linee ad alta corrente e a bassa tensione. Questa pratica riduce le interferenze elettromagnetiche di quasi il 75%. La schermatura di fili e cavi protegge i sistemi elettronici sensibili dalle interferenze.
Area di impatto | Approccio progettuale |
|---|---|
Gestione termica | Analisi CFD per ottimizzare il routing e ridurre al minimo l'accumulo di calore |
Compatibilità elettromagnetica | Separare le linee ad alta e bassa tensione, utilizzare la schermatura per ridurre le interferenze |
Nota: le interferenze elettromagnetiche possono disturbare i sistemi di comunicazione e le reti di sensori. La schermatura e un'attenta pianificazione dei percorsi garantiscono l'affidabilità del sistema.
Il funzionamento dei veicoli espone i cablaggi a vibrazioni e movimenti costanti. Gli ingegneri utilizzano metodi di fissaggio affidabili e staffe speciali per fissare i cablaggi. Progettano layout per evitare lunghezze o cortezze eccessive, riducendo al minimo l'attrito e l'usura. Le coperture protettive proteggono le aree vulnerabili dai danni ambientali. I sistemi di condotti a tre strati distribuiscono le sollecitazioni meccaniche. I tasselli antistrappo in silicone riducono le forze di estrazione nei punti critici. Queste strategie proteggono l'integrità dei connettori e prevengono l'affaticamento dei cavi, soprattutto in ambienti ad alta frequenza.
Una corretta progettazione del layout riduce al minimo l'attrito dovuto alle vibrazioni.
Staffe e metodi di fissaggio speciali impediscono il movimento dell'imbracatura.
Le coperture protettive e i sistemi di condotti aumentano la durata.
I progettisti danno priorità alla manutenzione e all'accessibilità in cablaggio del veicolo elettrico Sistemi. Utilizzano connettori che garantiscono connessioni corrette e facile accesso per la manutenzione. Il cablaggio organizzato previene le interferenze e semplifica la manutenzione. I layout tridimensionali ottimizzano lo spazio e consentono riparazioni più semplici. I materiali isolanti prevengono il contatto accidentale con le parti metalliche, migliorando la sicurezza. I materiali resistenti al calore e impermeabili garantiscono stabilità in condizioni estreme. Le caratteristiche di accessibilità facilitano lo smontaggio e il montaggio rapidi durante la manutenzione.
Caratteristica di progettazione | Beneficio |
|---|---|
Applicazione del connettore | Facile manutenzione e connessioni affidabili |
Fasciatura dell'imbracatura | Cablaggio organizzato, accesso semplice |
Layout tridimensionale | Spazio ottimizzato, riparazione più facile |
Materiali isolanti/resistenti al calore | Maggiore sicurezza e affidabilità |
Considerazioni sull'accessibilità | Smontaggio e montaggio rapidi |
Gli ingegneri selezionano i materiali conduttori e isolanti in base alle prestazioni elettriche, alla durata e al costo. Il rame rimane il conduttore preferito grazie alla sua eccellente conduttività e resistenza alla corrosione. L'alluminio offre un'alternativa leggera ed economica, soprattutto nelle applicazioni in cui la riduzione del peso è fondamentale.
Tipo di materiale | Vantaggi |
|---|---|
Rame (Cu) | Ottima conduttività, resistenza alla corrosione |
Alluminio (Al) | Leggero, conveniente |
XLPE | Isolamento superiore, resistenza meccanica, resistenza all'invecchiamento, rapporto costi-efficacia |
Gomma siliconica | Resistenza alle alte temperature, flessibilità |
L'isolamento in XLPE offre un'eccezionale resistenza alla tensione e alla resistenza meccanica. La gomma siliconica eccelle in ambienti ad alta temperatura e offre flessibilità per cablaggi complessi. Questi materiali garantiscono la sicurezza e l'affidabilità dei cablaggi ad alta tensione anche in condizioni difficili.
La scelta del cavo dipende da diversi criteri tecnici:
Il diametro del cavo deve corrispondere alla disposizione e alle caratteristiche dei componenti ad alta tensione.
Gli ingegneri aumentano la sezione trasversale per gestire correnti più elevate e ridurre le perdite resistive.
La tensione nominale garantisce che il cavo possa sopportare il carico elettrico senza guasti.
La resistenza al calore mantiene l'integrità dell'isolamento durante la trasmissione di correnti elevate.
Sezioni trasversali più ampie contribuiscono ad attenuare la maggiore resistività dell'alluminio, ma possono complicare l'installazione a causa delle dimensioni maggiori. Valori di tensione e resistenza al calore adeguati prevengono la rottura dell'isolamento e il guasto dei cavi, soprattutto nei veicoli elettrici che operano con carichi variabili.
Suggerimento: verificare sempre che i cavi siano conformi agli standard di sicurezza del settore, come i requisiti di assenza di alogeni e bassa emissione di fumi, per migliorare la sicurezza antincendio e la tutela ambientale.
I materiali di schermatura e guaina proteggono i cavi dalle interferenze elettromagnetiche e dagli ambienti difficili. Gli ingegneri utilizzano materiali all'avanguardia per garantire sicurezza e durata.
Tipo di materiale | Descrizione |
|---|---|
Foglio di alluminio-Mylar con fili di drenaggio | Schermatura EMI efficace |
Schermature in maglia di rame intrecciata | Protezione robusta dalle interferenze |
Nastro metallico avvolto a spirale | Opzione di schermatura flessibile |
TPU (poliuretano termoplastico) | Ottima resistenza all'abrasione, flessibilità |
Poliolefine ignifughe | Maggiore resistenza alla fiamma |
Composti HFFR | Ecologico, a basso contenuto di fumi, zero emissioni di alogeni |
I composti ritardanti di fiamma privi di alogeni (HFFR) offrono un'eccellente resistenza alla fiamma e sicurezza ambientale. Gli elastomeri termoplastici riciclabili (TPE) offrono flessibilità e prestazioni termiche, supportando al contempo gli obiettivi di sostenibilità. Questi progressi aiutano i produttori a soddisfare rigorosi standard di sicurezza e ambientali.
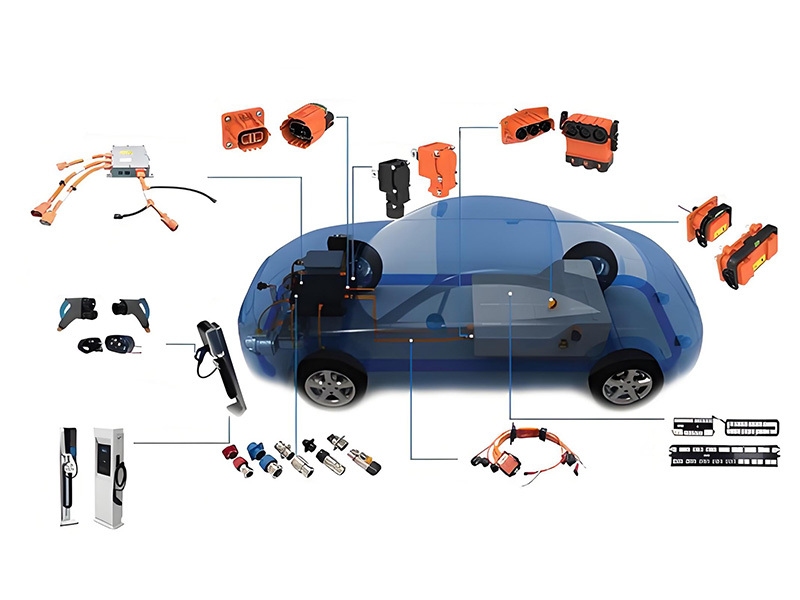

Gli ingegneri automobilistici selezionano connettori per autoveicoli ad alta tensione Basati su rigorosi criteri prestazionali per garantire l'affidabilità dei cablaggi ad alta tensione. I tipi di connettori più comuni includono connettori standard LV (bassa tensione), connettori USCAR e connettori JIS. Ogni tipologia soddisfa specifici standard di settore in termini di compatibilità e sicurezza.
I connettori devono garantire prestazioni elettriche, meccaniche e ambientali costanti. La tabella seguente riassume i requisiti essenziali:
Tipo di prestazione | Requisiti |
|---|---|
Prestazioni elettriche | La tensione nominale deve essere superiore alla tensione di picco. La corrente nominale deve essere superiore alla corrente operativa media. La resistenza di contatto e l'aumento di temperatura devono rispettare limiti rigorosi. |
Prestazioni meccaniche | I connettori devono resistere a oltre 50 cicli di inserimento/disinserimento. Affidabili meccanismi di bloccaggio impediscono la disconnessione accidentale. |
Prestazioni ambientali | I connettori devono resistere a sbalzi di temperatura, umidità e vibrazioni. Sono obbligatori un'adeguata protezione IP e proprietà ignifughe. |
Gli ingegneri danno priorità ai connettori che mantengono una pressione di contatto stabile e riducono al minimo la resistenza. Selezionano materiali resistenti alla corrosione e al degrado ambientale. Tecniche di produzione avanzate garantiscono precisione e durata, riducendo il rischio di guasti ai contatti elettrici e di rottura dell'isolamento.
Suggerimento: la scelta di connettori dotati di meccanismi di bloccaggio robusti e di elevati gradi di protezione IP aumenta sia la sicurezza che la longevità nelle applicazioni dei veicoli elettrici.
I connettori ad alta tensione devono essere conformi a rigorosi standard meccanici, elettrici e ambientali. Questi standard proteggono gli utenti e garantiscono un funzionamento affidabile anche in condizioni difficili.
I produttori aderiscono a standard di sicurezza che prevengono le scosse elettriche e garantiscono la protezione dell'utente. Gli standard prestazionali verificano che i connettori funzionino in modo affidabile in diversi ambienti. I requisiti di progettazione stabiliti dai principali produttori automobilistici garantiscono compatibilità e sicurezza su tutte le piattaforme di veicoli.
Tipo standard | Descrizione |
|---|---|
Standard di sicurezza | Previene le scosse elettriche e garantisce la sicurezza dell'utente. |
Standard di prestazione | Garantire un funzionamento affidabile in diverse condizioni. |
Requisiti di progettazione | Garantire la compatibilità e la sicurezza attraverso criteri di progettazione specifici. |
Gli ingegneri sono consapevoli che la qualità dei connettori ad alta tensione influisce direttamente sulle prestazioni elettriche. La precisione di fabbricazione influenza l'affidabilità meccanica. Le prestazioni ambientali rimangono fondamentali per la sicurezza su strada.
I connettori ad alta tensione devono soddisfare elevati standard di qualità e precisione di fabbricazione.
Questi connettori sono considerati prodotti di fascia alta per il loro ruolo fondamentale nella sicurezza dei veicoli.
I produttori implementano rigorosi protocolli di test per verificare l'affidabilità dei connettori. Analizzano le modalità di guasto, come contatti insufficienti, guasti all'isolamento e problemi di connessione meccanica. Strumenti diagnostici avanzati, come il software di diagnostica topologica, aiutano a identificare e dare priorità ai guasti dei connettori, semplificando la manutenzione e riducendo i tempi di fermo.
Le funzionalità di sicurezza nei connettori ad alta tensione proteggono sia gli utenti che i sistemi del veicolo. Gli ingegneri integrano la tecnologia High-Voltage Interlock Loop (HVIL) per proteggere le persone durante l'assemblaggio, la riparazione e il funzionamento. L'HVIL funge da interruttore automatico, avvisando i conducenti in caso di compromissione di una connessione ad alta tensione. Il sistema monitora i connettori con un loop a bassa tensione, segnalando eventuali problemi in caso di interruzione del segnale.
HVIL garantisce che il sistema non possa essere acceso se il circuito è incompleto, aumentando la sicurezza.
Le tecnologie di disconnessione a prova di dita e di contatto impediscono il contatto accidentale con componenti ad alta tensione.
I connettori con fusibile scollegano la batteria durante i picchi di corrente, prevenendo eventi catastrofici.
La manutenibilità rimane un fattore chiave nella progettazione dei connettori. I pin sostituibili sul campo riducono al minimo i tempi di fermo e migliorano la produttività consentendo l'assistenza in loco. I connettori con una lunga durata, fino a 50.000 cicli, riducono il costo totale di proprietà. Il design ergonomico facilita l'utilizzo con una sola mano, riducendo il rischio di lesioni da movimenti ripetitivi. Le connessioni rapide possono essere effettuate senza utensili aggiuntivi, migliorando l'efficienza durante la manutenzione.
Caratteristica | Beneficio |
|---|---|
Pin sostituibili sul campo | Riduce al minimo i tempi di inattività e aumenta la produttività consentendo l'assistenza in loco. |
Lunga durata (fino a 50.000 cicli) | Riduce il costo totale di proprietà prolungando la durata dei connettori. |
Design ergonomico | Facilita l'utilizzo con una sola mano, riducendo il rischio di lesioni dovute a movimenti ripetitivi. |
Collegamenti rapidi | Garantisce connessioni sicure e veloci senza bisogno di strumenti aggiuntivi, migliorando l'efficienza. |
Gli ingegneri affrontano le più comuni modalità di guasto, come guasti ai contatti elettrici, guasti all'isolamento, contaminazione, archi elettrici e danni fisici. Selezionano materiali resistenti alla corrosione e al degrado ambientale. Un'attenta progettazione migliora la robustezza dei connettori, mentre rigorosi protocolli di collaudo garantiscono affidabilità e sicurezza.
Nota: il corretto collaudo e la corretta gestione dei cablaggi e dei connettori ad alta tensione sono fondamentali per evitare guasti durante il funzionamento. Metodi diagnostici avanzati e un'attenta selezione dei materiali contribuiscono a preservare l'integrità del sistema e la sicurezza del veicolo.
Gli ingegneri del settore automobilistico raggiungono livelli ottimali di sicurezza e affidabilità seguendo le migliori pratiche del settore per cablaggi e connettori ad alta tensione. Identificano i requisiti elettrici, creano schemi dettagliati e utilizzano la modellazione CAD per un routing preciso. Il rispetto degli standard internazionali riduce rischi come cortocircuiti e interferenze elettromagnetiche. La seguente checklist evidenzia i passaggi essenziali della progettazione:
Elemento della lista di controllo | Descrizione |
|---|---|
La sicurezza viene prima di tutto | Prevenire le scosse elettriche e garantire un percorso sicuro in caso di incidente. |
Gestione termica | Utilizzare un isolamento resistente al calore e ottimizzare i percorsi dei cavi. |
EMI e interferenze del segnale | Separare i circuiti AT e BT; applicare la schermatura. |
Ottimizzazione del peso | Ridurre al minimo la lunghezza dei cavi e prendere in considerazione conduttori leggeri. |
Produzione e manutenzione | Progettato per connessioni a prova di errore ed etichettatura chiara. |
L'applicazione di questi principi migliora le prestazioni del veicolo, la sicurezza e la conformità agli standard del settore.
Gli ingegneri automobilistici seguono standard come USCAR, JIS e LV. Questi standard garantiscono compatibilità, sicurezza e affidabilità. Specificano i requisiti di tensione, corrente, durata meccanica e resistenza ambientale.
Utilizzano materiali isolanti ad alta resistenza alla tensione. Sono dotati di schermatura per ridurre le interferenze elettromagnetiche. Dispositivi di sicurezza come HVIL e robusti meccanismi di bloccaggio impediscono il contatto e la disconnessione accidentali.
Il rame offre una conduttività e una resistenza alla corrosione superiori. Supporta un'erogazione di potenza stabile e riduce le perdite di energia. L'alluminio offre un'alternativa leggera, ma richiede una sezione trasversale maggiore per ottenere le stesse prestazioni.
Ispezioni regolari rilevano tempestivamente usura, corrosione o collegamenti allentati. Gli ingegneri raccomandano di pulire i contatti, controllare le guarnizioni e sostituire i componenti danneggiati. Una corretta manutenzione garantisce un funzionamento affidabile e riduce il rischio di guasti.